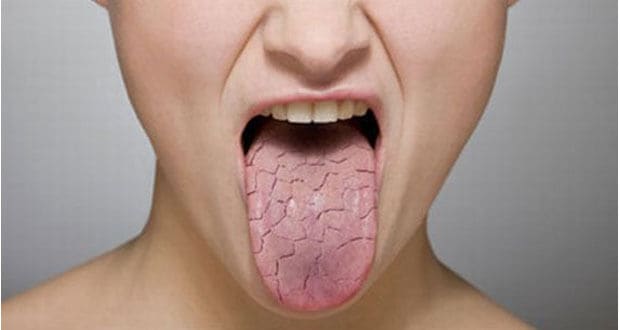
Dry mouth?
Xerostomia is the subjective sensation of oral dryness due to the decrease of saliva, caused by an alteration of the functioning of the salivary glands.
The presence of saliva in the oral cavity is very important because it keeps the oral tissues moist, facilitating speech, chewing, swallowing, etc. Saliva also allows the mouth cleaning function as well as regulation of bacterial buildup. A suitable level of saliva can prevent an imbalance of microorganisms in the oral environment that can lead to the appearance of cavities, gum disease, halitosis or bad breath, among others.
Xerostomia manifests itself in one in five adults, equivalent to 20% of the population between 18 and 30 years old, and 40% in those over 50 years of age. It should be noted that it affects twice as many women as men. According to statistical data, xerostomia is increasingly taking a leading role in society. It is a condition that alters the general health and quality of life.
By itself, dry mouth is not considered a disease; however, it may be a symptom of medical conditions, or even the side effect of a common medication.
Saliva helps protect against dry mouth, if your saliva flow is reduced, the resulting of having a dry mouth can lead to serious problems because your remaining saliva may be unable to perform its important functions in your mouth. Some of the major functions of saliva include:
- Helping kill harmful bacteria
- Keeping your mouth moist
- Removing remnants of food and maintaining your mouth’s cleanliness
- Strengthening your teeth by restoring important minerals.
There are also two types of Xerostomia to consider – one type is reversible, and one is permanent.
- Reversible xerostomia is characterized by recording residual glandular activity, where salivary secretion can be stimulated or regulated. This type of xerostomizing effect is produced by medications, chemotherapeutic, smoking, etc.
- In irreversible xerostomia, there is irreparable damage to the glandular level that prevents its functioning. This clinical picture can be found in patients with diagnosis of Sjögren’s syndrome or patients with head and neck cancer who receive as treatment large doses of radiation.
The effects of dry mouth could be mild, moderate or severe, and it may cause minor or major discomfort. The most frequent are the following:
- Normally speaking in public increases the need for salivation to help vocalize words better, and prolonging over time can lead to lack of saliva and the need to ingest liquids.
- Stress, anxiety and depression affect the central nervous system and, therefore, organs and glands are affected throughout the body, including salivary.
- Diabetes and other systemic diseases also affect the whole organism, altering glandular functioning.
- Therapy with certain drugs such as antihistamines, antihypertensives, diuretics; And oncological drugs, have as collateral effects the decrease of the saliva and even the atrophy of the mucous glands.
- On the other hand, the absence of teeth causes a decrease of stimuli in the mouth and, as a consequence, there is a lower production of saliva.
- In addition, an unbalanced diet with excess carbohydrates and deficits in fruits and vegetables can cause alteration of saliva production.
- Smoking and alcohol consumption may also decrease salivary secretion, as it inhibits the transmission of nerve impulses.
The most frequent difficulties are presented during: chewing, swallowing, phonation, and alterations of taste, pasty mouth upon awakening, burning mouth.
The decrease of the saliva makes the soft tissues more susceptible to the dryness, redness, irritation, presence of cracks, facilitating the attack of the opportunistic microorganisms. This in turn favors inflammation of the mucous membranes (mucositis), inflammation of the gums (gingivitis), presence of painful ulcerations and local infections caused by fungi such as candidiasis, fissures in the lips, halitosis. It is frequently related to pharyngitis, laryngitis, dyspepsia or even constipation.
The main effects of decreased salivary flow on the dental tissue are increased carious lesions and dental sensitivity. In patients with xerostomia with dental implants, rubbing causes erosions on the buccal mucosa. When this happens, we urge you to call our office for a consultation.
It is so important to treat dry mouth to avoid serious health problems. It is very important to visit your dentist; oral hygiene is essential in case of dry mouth, oral hygiene techniques should be strengthened by using a dental brush with soft filaments.
For more information in regards to Dry mouth or Xerostomia please contact Dr. Mauricio Hervas at Implantation Dental Center to 954.476.0770.